ScoreBoard and Tomasulo Alogorithm
ScoreBoard 和 Tomasulo 算法是体系结构中 指令级并行(ILP: Instruction Level Parallelism) 内容必磕的两个算法。
ScoreBoard Algorithm
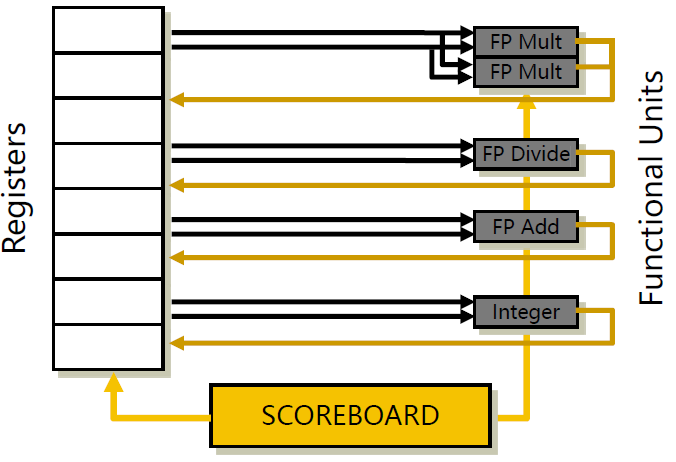
记分板体系结构
首先让我们看一看 ScoreBoard 的三个部件:
- Instruction status: which of 4 steps the instruction is in
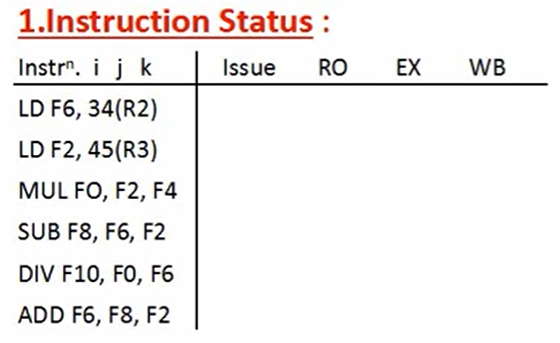
Instruction status
- Functional unit status: Indicates the state of the functional unit (FU). 9 fields for each functional unit
- Busy—Indicates whether the unit is busy or not
- Op—Operation to perform in the unit (e.g., + or –)
- Fi—Destination register
- Fj, Fk—Source-register numbers
- Qj, Qk—Functional units producing source registers Fj, Fk (理解为 Fj,Fk 在
Register result status中的functional unit,即某个functional unit占用 Fj 或者 Fk) - Rj, Rk—Flags indicating when Fj, Fk are ready
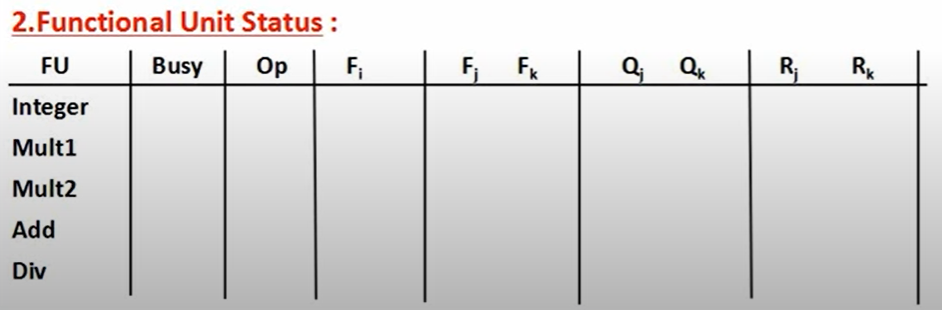
Functional unit status
- Register result status—Indicates which functional unit will write each register, if one exists. Blank when no pending instructions will write that register
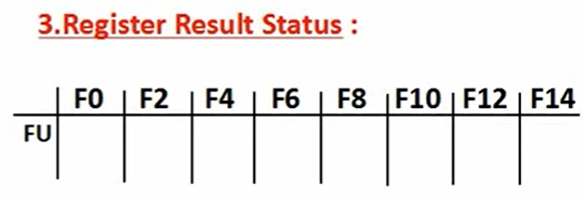
Register result status
看过ScoreBoard 的部件设计图后,我们来了解一下它的设计思想:
Overview
基本思想
- Use
scoreboardto track data (RAW) dependence through register (使用ScoreBoard追踪寄存器间的 RAW 数据相关。)
主要的设计思想
- Instructions are sent to FU unit if there is no outstanding name dependence. (如果指令没有名称冲突,则将指令送到 FU)
- RAW data dependence is tracked and enforced by scoreboard. (RAW 数据相关会被 Scoreboard 追踪)
- Register values are passed through the register file; a child instruction starts execution after the last parent finishes execution. (寄存器值通过寄存器文件传递,父指令执行完后子指令开始执行)
- Pipeline stalls if any name dependence (WAR or WAW) is detected. (如果检测到 WAR,WAW冲突,冲突的两个指令中,执行顺序中应当后执行的指令的流水线会暂停)
算法执行步骤
- Issue—decode instructions & check for structural hazards
- No Wait conditions: (1) the required FU is free; (2) no other instruction writes to the same register destination (to avoid WAW)
- Actions: (1) the instruction proceeds to the FU; (2) scoreboard updates its internal data structure
- If an instruction is stalled at this stage, no other instructions can proceed
- Read operands—wait until no data hazards, then read operands
- Wait conditions: all source operands are available
- Actions: the function unit reads register operands and start execution the next cycle
- The scoreboard resolves RAW hazards. dynamically in this step, and instructions may be sent into execution out of order
- Execution—operate on operands (EX)
- Actions: The functional unit begins execution upon receiving operands. When the result is ready, it notifies the scoreboard that it has completed execution.
- Write result—finish execution (WB)
- Wait condition: no other instruction/FU is going to read the register destination of the instruction
- Actions: Write the register and update the scoreboard
- the scoreboard checks for WAR hazards. If none, it writes results. If WAR , then it stalls the instructions
Example
算法执行步骤可能有点复杂,不要担心,在YouTube上找到一个十分直观的例子来理解上述算法执行步骤,结合这个例子,可以帮助理解算法执行步骤。
Tomasulo Algorithm
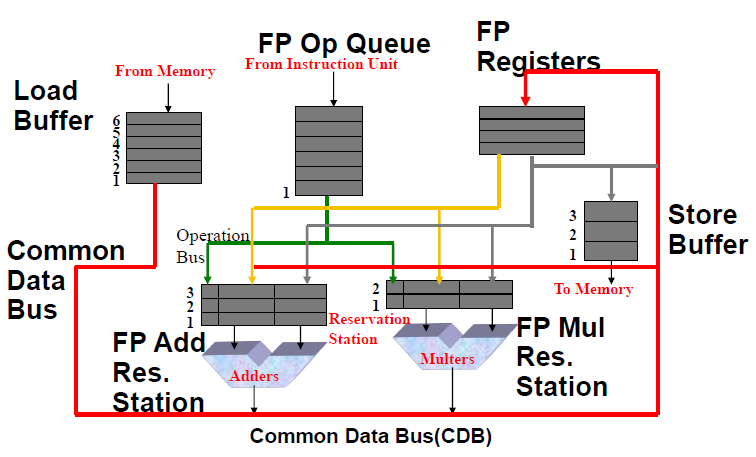
Tomasulo架构图
Tomasulo 算法是 ScoreBoard算法的改进
Overview
基本思想
- 消除指令执行过程中的数据相关
- 指令调度过程中引入
tag-broadcasting
主要的设计思想
- 功能缓冲部件称为了保留站(reservation stations),用来存放计算的操作数。
- 指令中的寄存器被数值或者指向保留站的指针代替,这一过程称为:寄存器换名(register renaming)
- 消除 WAR,WAW 冒险
- 保留站比实际寄存器多,可以完成编译器不能完成的优化工作
- 结果从保留站直通 FU,无需通过寄存器,而是通过公共数据总线(Common Data Bus)把结果广播到所有的 FU
- 装入(Load)和存储(Stores)也像其他部件一样具有保留站(专门的缓冲器)
保留站组成部分
- Op—Operation to perform in the unit (e.g., + or –)
- Qj, Qk—Reservation stations producing source registers (value to be written)
- Vj, Vk—Value of Source operands
- Rj, Rk—Flags indicating when Vj, Vk are ready
- Busy—Indicates reservation station and FU is busy
- Register result status—Indicates which functional unit will write each register, if one exists. Blank when no pending instructions that will write that register.
算法执行步骤
- Issue—get instruction from FP Op Queue
- If reservation station free (no structural hazard), the scoreboard issues instr & sends operands (renames registers, solve WAR WAW)
- Execution—operate on operands (EX)
- When both operands ready then execute; (solve RAW)
- if not ready, watch CDB for result
- Write result—finish execution (WB)
- Write on Common Data Bus to all awaiting units;
- mark reservation station available
- Normal bus: data + destination
- Common Data Bus: data + source
- Normal = “Go To” bus; CDB = “Come From” bus
Example
可能看的还是有些晕乎,不要担心,还是结合直观的例子来帮助理解算法执行步骤。
扩展阅读
知乎上看到理解现代处理器:指令级并行篇,从“从数据流动态分析”的角度理解指令集并内容更加直观